xAI’s Grok 1.5 gets a vision upgrade: Can process images and generate code from a diagram

Just two weeks after Elon Musk’s AI venture xAI unveiled Grok-1.5, Musk’s persistent push to validate open-source AI’s prowess against the titans of the field receives a fresh boost with Grok’s latest evolution. This time, xAI has released Grok-1.5 Vision, a groundbreaking upgrade that catapults xAI into the forefront of multimodal AI innovation.
Over the weekend, xAI released Grok-1.5 Vision, a multimodal enhancement to open-source models, empowering it to decode visual information. Surpassing its predecessors and rivals, this latest iteration equips Grok with the ability to process visual information, marking a pivotal moment in its evolution and positioning xAI as a heavyweight contender in the AI space.
Grok-1.5 Vision boasts the capacity to analyze a wide array of visual data, including documents, diagrams, charts, screenshots, and photographs, with a focus on real-world comprehension. The rollout of Grok-1.5V signals xAI’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of AI capabilities and underscores its dedication to providing users with cutting-edge technology.
Grok-1.5 Vision Capabilities
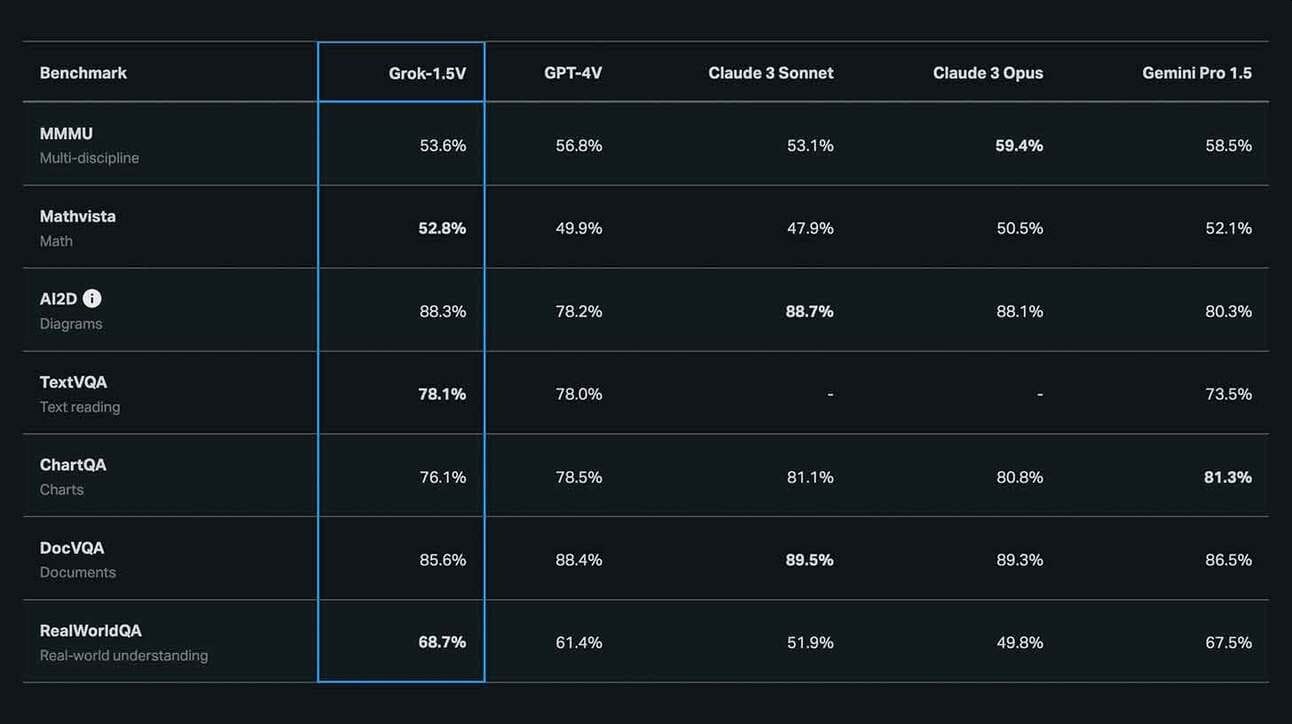
Among its standout features, Grok-1.5V shines in its understanding of the physical world, surpassing its peers in the newly introduced RealWorldQA benchmark designed to evaluate spatial understanding. Leveraging its prowess in multi-disciplinary reasoning, Grok sets a new standard for performance in processing various forms of visual data.
“Grok-1.5V is competitive with existing frontier multimodal models in a number of domains, ranging from multi-disciplinary reasoning to understanding documents, science diagrams, charts, screenshots, and photographs. We are particularly excited about Grok’s capabilities in understanding our physical world. Grok outperforms its peers in our new RealWorldQA benchmark that measures real-world spatial understanding. For all datasets below, we evaluate Grok in a zero-shot setting without chain-of-thought prompting,” xAI said in a release note.
Notably, xAI’s decision to introduce the RealWorldQA benchmark underscores its commitment to transparency and accountability in AI development. By evaluating Grok’s capabilities in a zero-shot setting without chain-of-thought prompting, xAI aims to provide users with a comprehensive assessment of its performance across different domains.
Generating Code From a Diagram
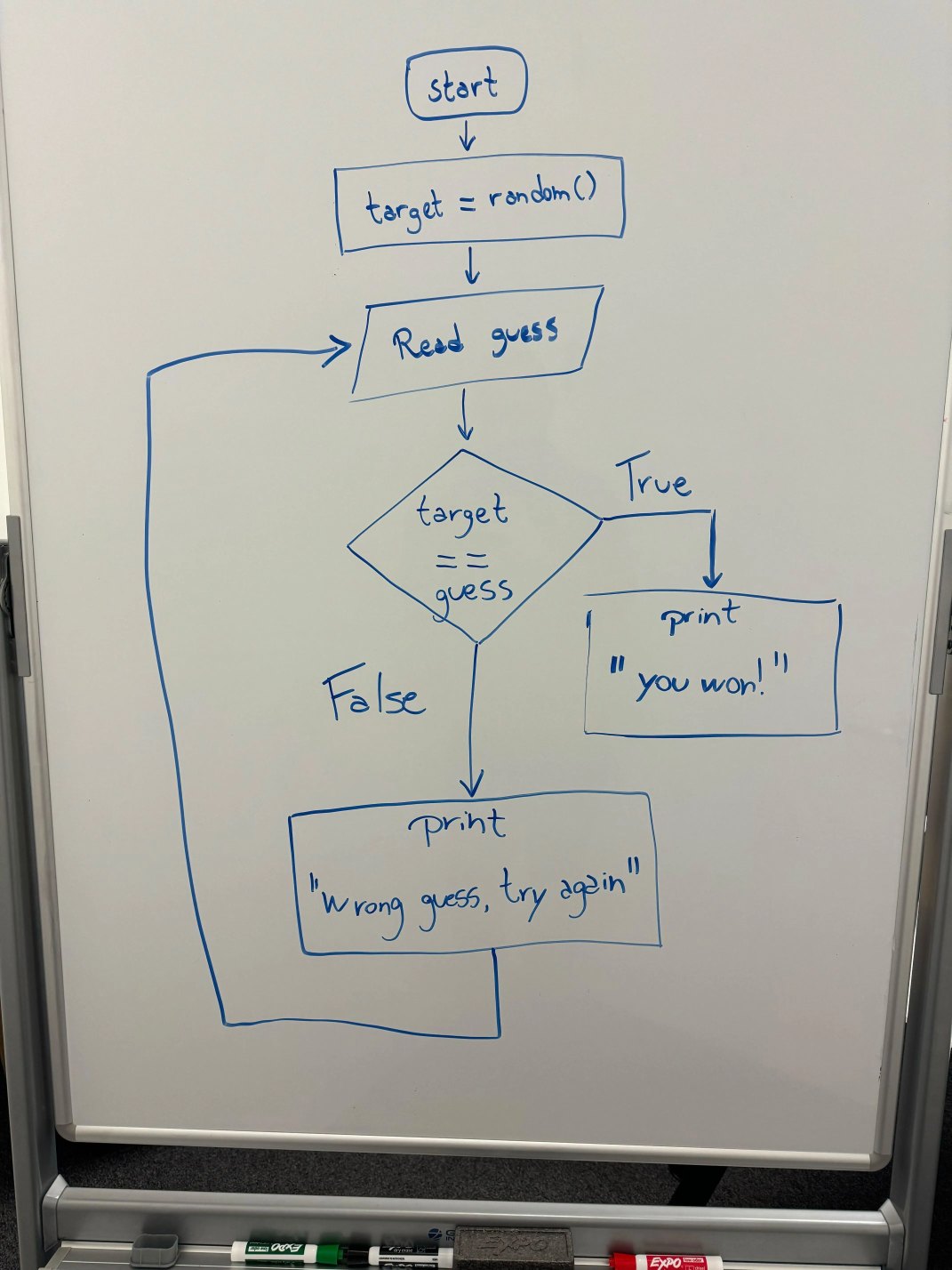
In addition to processing images, Grok 1.5 can also write code from a diagram. Below is a sample code generated by Grok based on a flowchart diagram.
User: Can you translate this into Python code?
Grok: Certainly! The flowchart you’ve provided describes a simple guessing game where the computer generates a random number, and the user has to guess it. Here’s the Python code that represents the logic in the flowchart:
Below is the generated Pyhton code:
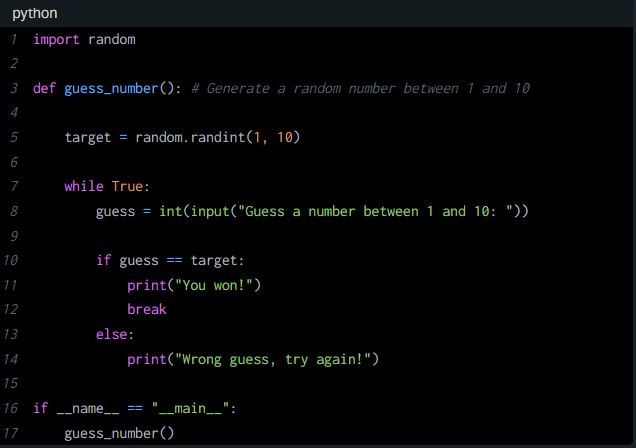
This piece of code executes the guessing game outlined in the flowchart. It prompts the user to input their guess repeatedly until they correctly guess the number.
Overall, as xAI prepares to roll out Grok-1.5V to testers and existing users in the coming weeks, anticipation is high for the anticipated improvements across images, audio, and video. Despite Grok’s somewhat subdued presence in broader discussions surrounding large language models, its impressive vision upgrade serves as a testament to the growing influence of open-source models in the AI landscape.
Backed by Elon Musk’s vast reservoir of data from ventures like X and Tesla, xAI is poised to disrupt the status quo and demand attention from industry players. With Grok leading the charge, the era of open-source AI supremacy may be closer than we think.

