Mitsubishi Electric Develops Compact AI Knowledge Representation and Reasoning Solution for Human-Machine Interfaces

TOKYO, January 28, 2020 – Mitsubishi Electric Corporation (TOKYO: 6503) announced today it has developed a compact knowledge representation and reasoning solution designed for deployment in embedded human-machine interfaces. Based on the company’s Maisart®* artificial intelligence (AI) technology, the new development enables edge devices to understand vague user commands through the extrapolation of missing information. It achieves this by means of a “knowledge graph” which integrates user information, device specification and functionality and external information, and will allow responsive and easy-to-use human-machine interfaces to be embedded in consumer products such as televisions and car navigation systems.
- *Mitsubishi Electric’s AI creates the State-of-the- ART in technology

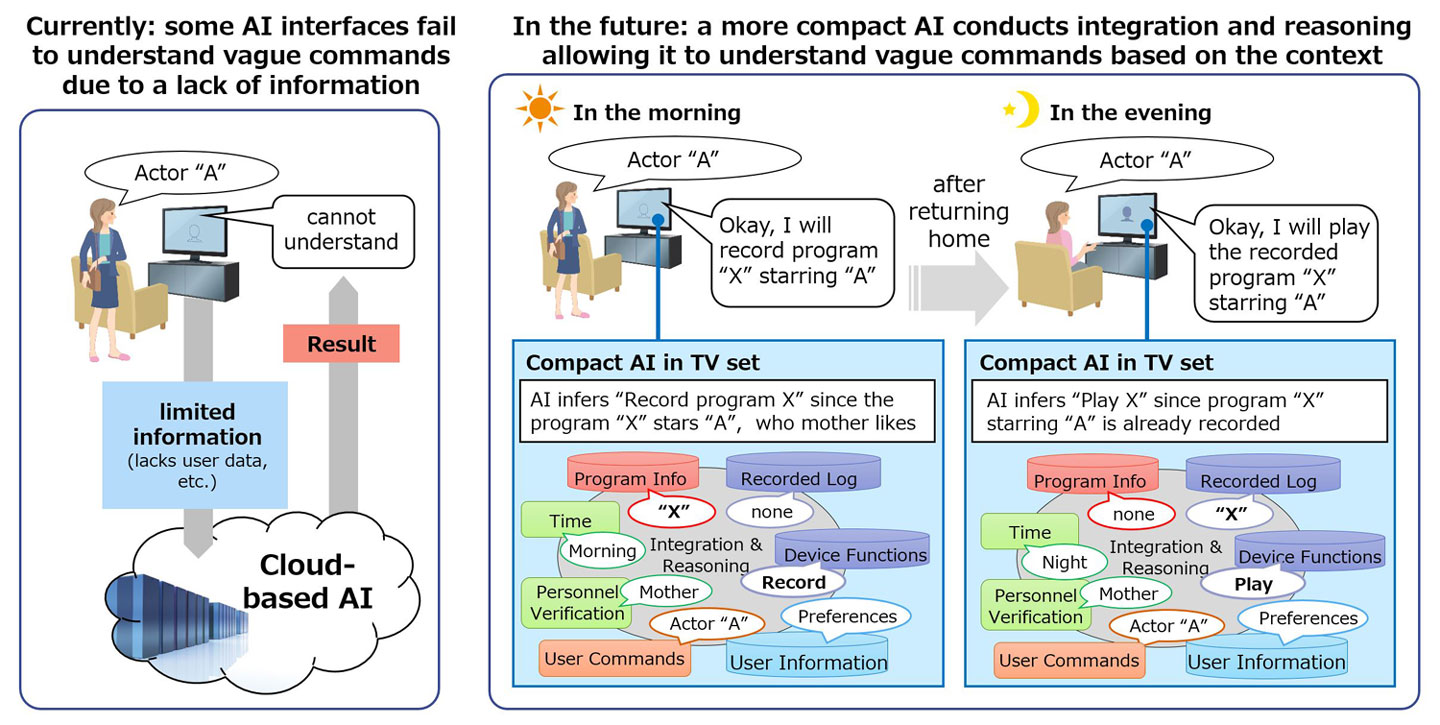
Fig 1: Example of application used in a television
Key Features
- 1)Understands vague commands by deducing missing information using a knowledge graphhis new technology allows missing information in voice commands to be deduced by means of a knowledge graph. This is a database that expresses the relevance of information using three sets of components-subjects, predicates and objects-where user information, device specifications and functionality and external information are integrated.
For example, as in fig. 1, when a user issues just the instruction “Actor A” to their television before going out in the morning, the newly developed solution contained in the device will respond, “I will record the program ‘X’ starring actor ‘A'”. In this example, the artificial intelligence embedded in the solution deduces the lacking information as follows. First, using its cameras it identifies the user as the “mother”. It then retrieves from the knowledge graph the information that the mother’s favorite program is X, the program X stars Actor A, it starts from 10 AM, the mother will not be able to watch the program because of her daily schedule, and it is not currently due to be recorded. Finally, by using this information, the system infers that the mother wants to record program X and takes appropriate action.
- 2)Compact reasoning technology enables quick HMI response in edge devicesAs part of this new solution, Mitsubishi Electric has developed a reasoning methodology that reduces the amount of computation and memory usage required to interpret vague commands. It achieves this through a reduction in the size of the required knowledge graph by adjusting its relevance with reference to user commands and sensing information. This allows a fast and responsive human-machine interface on edge devices.
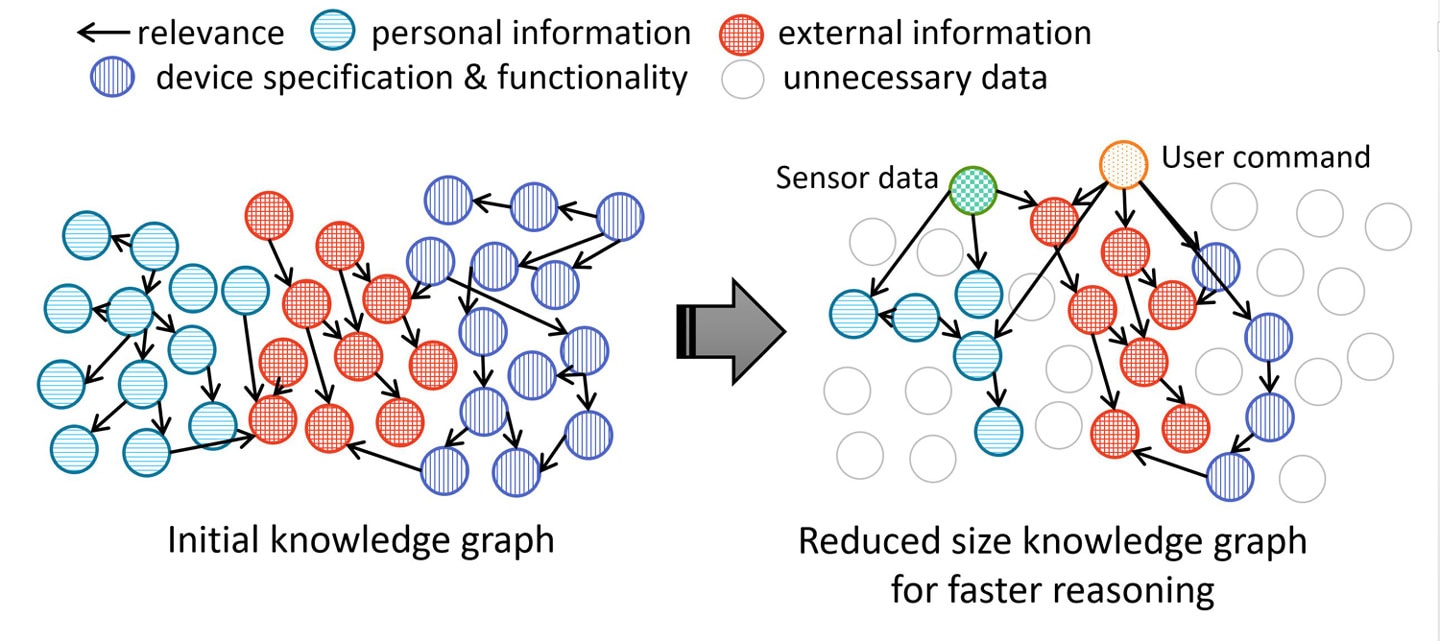
Fig. 2: Overview of knowledge graph reduction
Future Developments
Mitsubishi Electric intends to initially deploy this new technology in home appliances and car navigation systems, aiming to commercialize it from 2022 onwards. In the future, the company will consider applying the technology to inquiries and quality control processes within Mitsubishi Electric’s own internal operations.