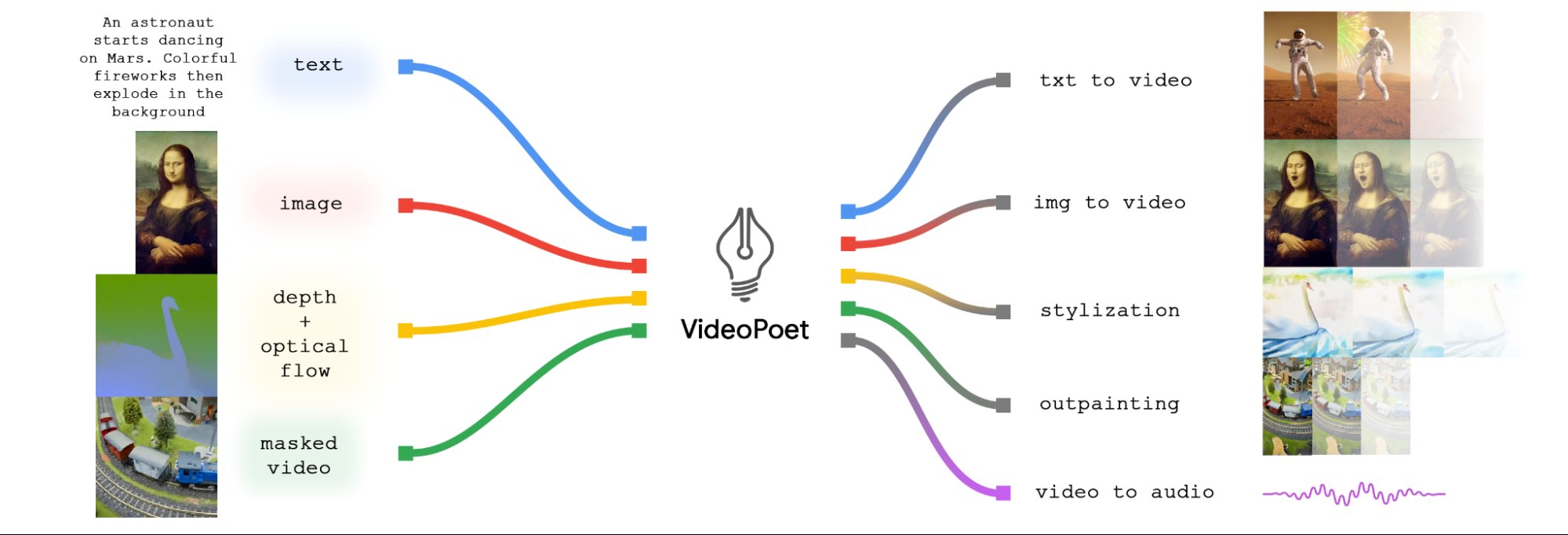
VideoPoet: Google looks to challenge OpenAI Sora and Stable Diffusion for dominance in AI video creation
Posted On April 12, 2024
0
2.3K Views