Google deindexed 2% of sites in its March Update as it cracks down on AI-generated content, Originality AI study finds

Earlier this month, we covered Google after the search giant cracked down on expired domains used for SEO manipulation. The move quickly sent shockwaves through the digital marketing community. The action was part of Google’s broader March Content Update aimed at combating spammy, low-quality, and AI-generated content saturating search engine results.
Fast forward two weeks later, the repercussions of Google’s actions are becoming increasingly apparent. Fresh insights from two new studies conducted by Originality AI shed light on the aftermath of the crackdown and the extent of Google’s manual deindexing spree during its March Content Update.
Websites Deindexed by Google in March 2024
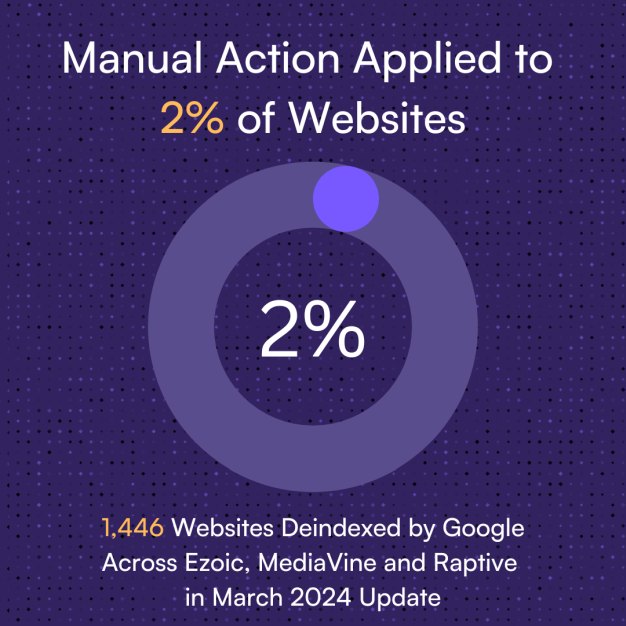
According to Originality AI studies, Google manually deindexed approximately 2 percent of websites during its March Content Update. Study 1, which analyzed 79,000 websites, revealed that 1,446 sites faced manual actions. Meanwhile, Study 2 delved deeper into the prevalence of AI-generated content among these penalized websites, uncovering that all of them hosted AI-generated posts, with half comprising a staggering 90%-100% of AI-generated content.
Originality.AI’s findings provide a stark snapshot of the fallout. As part of its studies, Originality AI checked several websites based on the company providing the advertising, including:
- MediaVine: 21,808
- Raptive: 6,428
- Ezoic: 51,293
The genesis of this upheaval traces back to March 5th, when Google announced its intent to slash unhelpful content by 40%. This initiative commenced with a barrage of manual actions levied against websites, resulting in their complete deindexing from Google’s search results. According to Google, when a site falls short of Google’s guidelines, it risks facing a “manual action,” leading to its removal from search results, or deindexing.
These manual actions, distinct from the forthcoming algorithm update, have been steadily rolling out over a span of 2 to 4 weeks. Notifications of these manual actions began flooding into websites’ Google Search Console Manual Action dashboards starting March 5th.
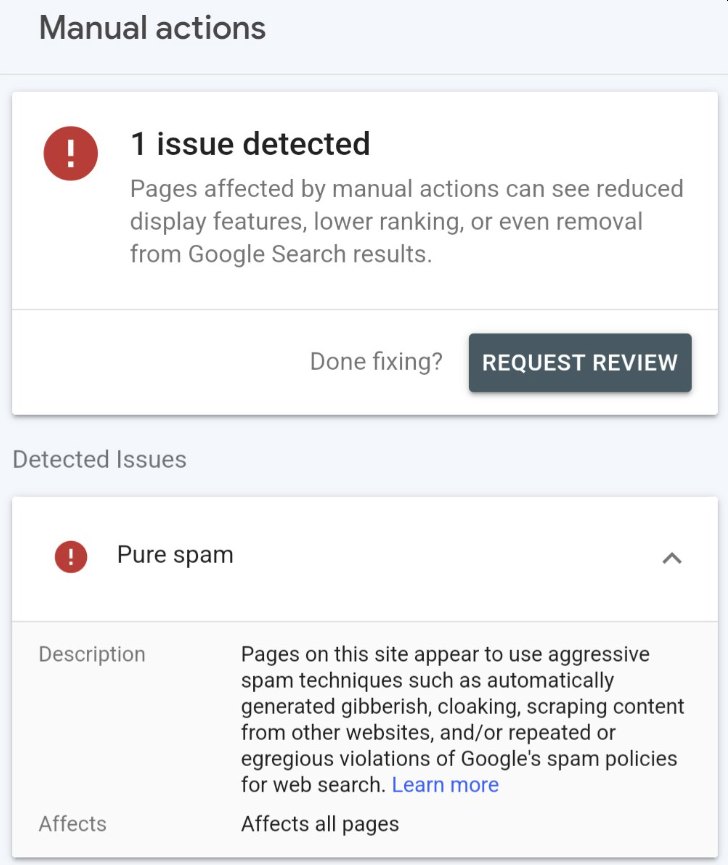
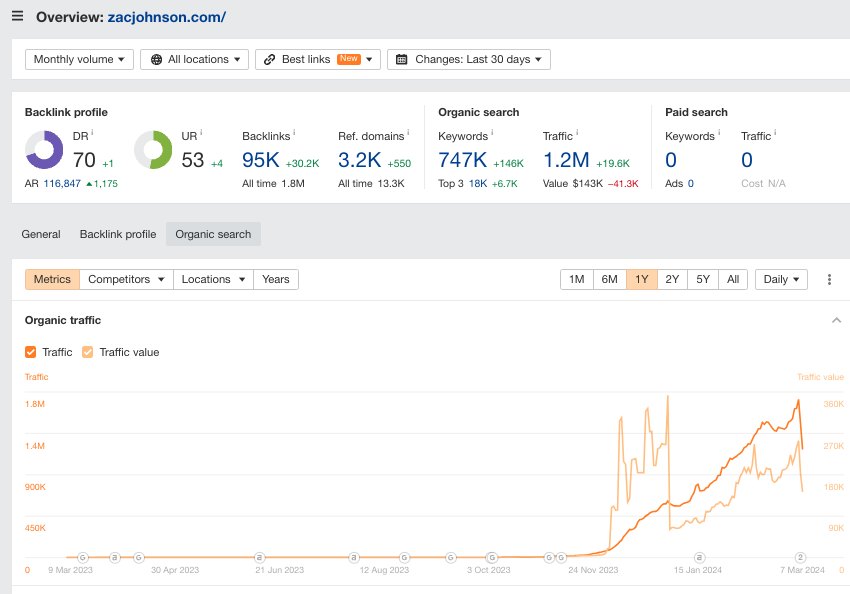
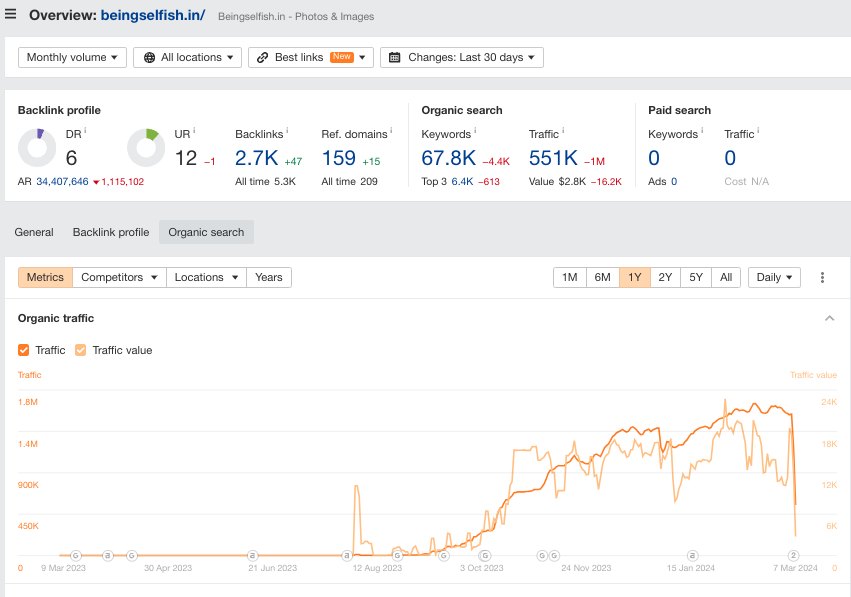
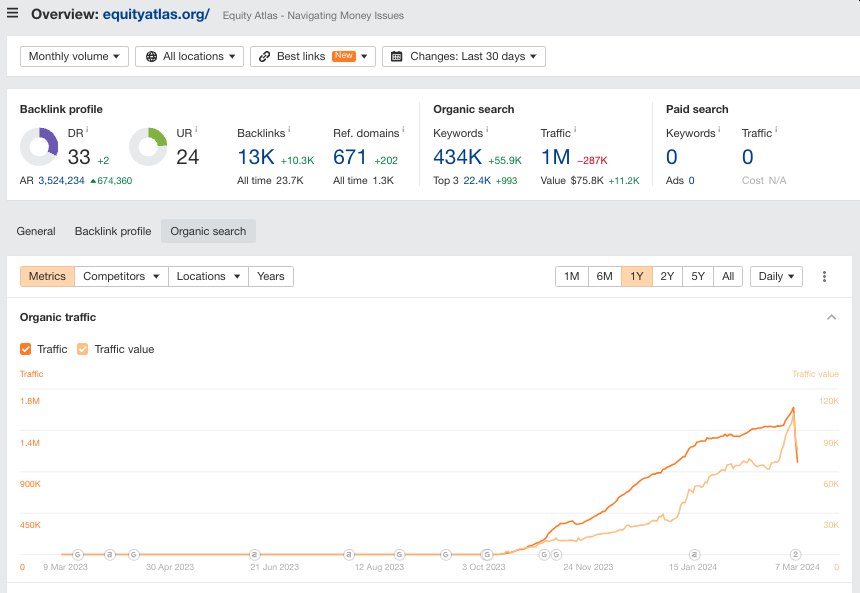
Study 1 focused on content-centric websites, excluding e-commerce platforms and others, and discovered over 1,446 sites hit with manual actions. These websites, previously enjoying Google Organic traffic, suffered a collective traffic loss estimated at over 20 million visitors per month. Notably, three websites witnessing a drastic plunge from over 1 million organic visitors monthly to zero were identified:
- zacjohnson.com
- beingselfish.in
- equityatlas.org
Study 1 Findings:
- Manual Action Applied to Over 1,446 sites that were on MediaVine, Raptive or Ezoic
- Of the approx 79k sites checked 1.9% of them had a manual action applied to them
- Cumulative traffic loss estimated at over 20 million visitors/month
- 3 websites With Over 1 Million Organic Visitors Per Month to Zero
Amidst speculations about Google’s motives, many in the media speculated that the update aimed to quash AI spam in search results.
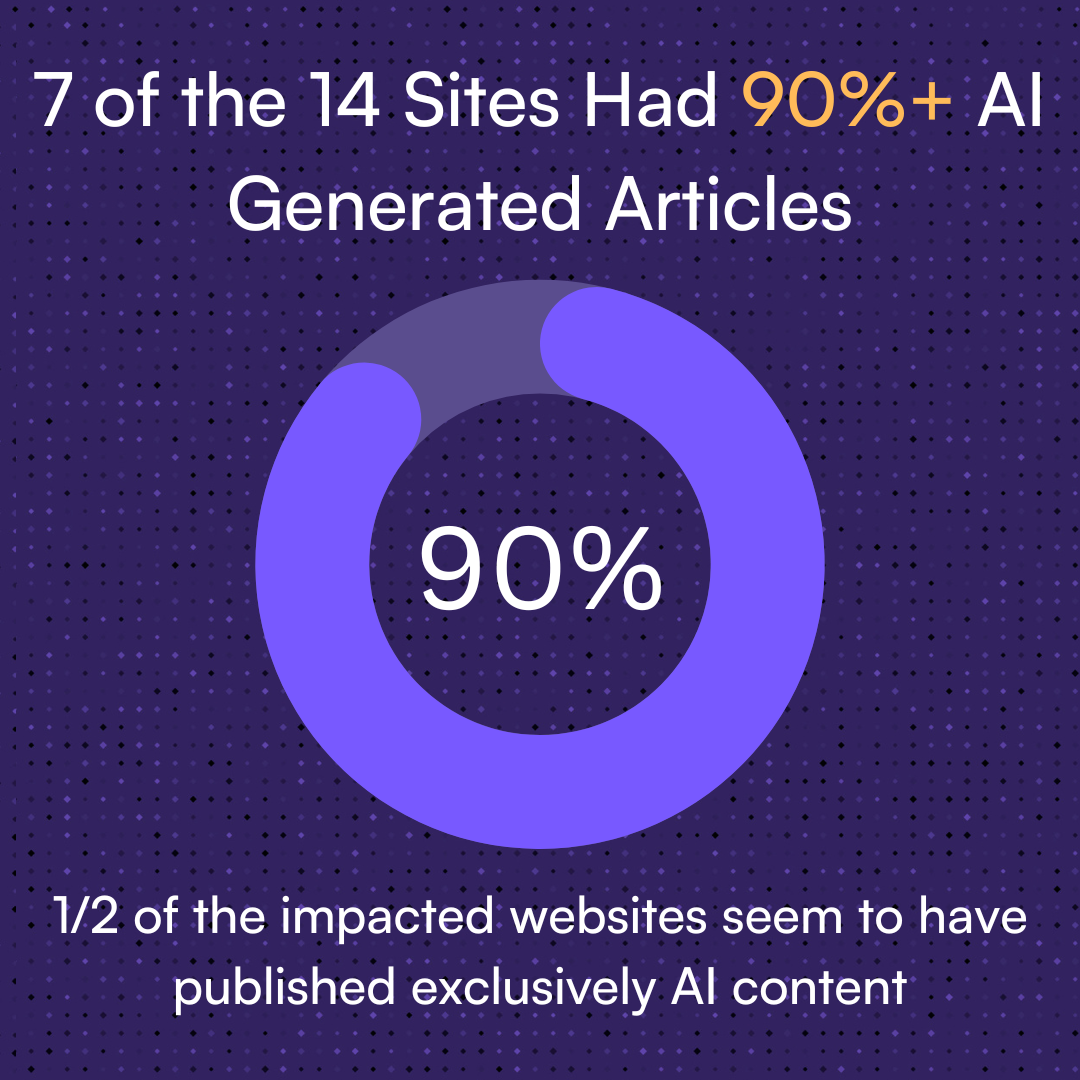
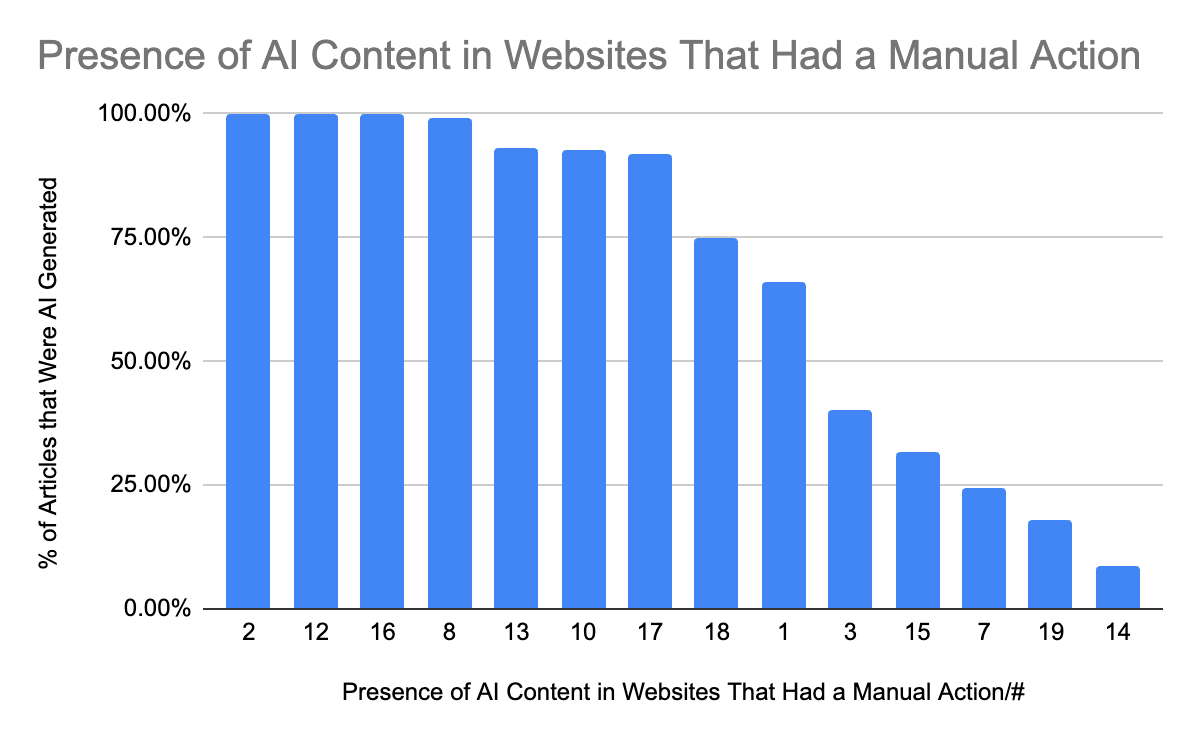
In Study 2, Originality.AI scrutinized whether AI-generated content was indeed the culprit behind the manual actions. Analyzing 100 recent articles from each deindexed site, the study found a pervasive use of AI content across all penalized sites, with 7 out of 14 sites displaying over 90% AI-generated content.
Study 2 Findings:
- 100% of Websites that Had Manual Action showed signs of using AI
- 7 of the 14 websites we analyzed had over 90% of their sample articles

Methodology:
Originality.AI’s methodology involved identifying deindexed sites and examining publicly shared URLs. Notably, all deindexed sites showed signs of AI usage, according to the study’s findings.
Google’s swift action against AI-generated spam underscores its commitment to maintaining the integrity of search results. As the battle against spam escalates, Google’s stance against AI-generated content appears resolute, signaling a proactive stance against this existential threat to its search ecosystem.
- Identified sites that were deindexed and whose URL was already disclosed on X
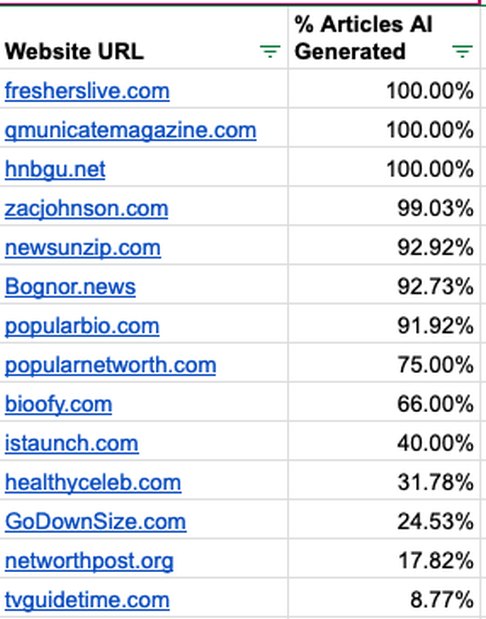
- fresherslive.com
- qmunicatemagazine.com
- hnbgu.net
- zacjohnson.com
- newsunzip.com
- Bognor.news
- popularbio.com
- popularnetworth.com
- bioofy.com
- istaunch.com
- healthyceleb.com
- GoDownSize.com
- networthpost.org
- tvguidetime.com
- thesocialtalks.com
- juliangoldie.com
- chipperbird.com
- EquityAtlas.org
- filmifeed.com
- Scraped 100 of the most recent posts that are over 100 words long
- Several sites were excluded:
- juliangoldie.com – no longer fully deindexed – 10 pages are in the index (but publicly admits to using AI)
- chipperbird.com – unable to get content (but the website owner publicly admits to using AI)
- equityatlas.org – unable to get content
- filmifeed.com – unable to get content
- thesocialtalks.com – unable to get content
- Ran each article through our AI detector (detector efficacy) using model 2.0 Standard on March 7th
- Completed an analysis for each site to identify the Average AI score and the % of articles suspected of being AI-generated.
Conclusion
The implications of these findings reverberate across the digital landscape, sparking speculation regarding Google’s motives behind this crackdown. While many media outlets swiftly attributed the initiative to combating AI spam, the second study by Originality.AI delves deeper into the correlation between AI content and manual penalties.
In conclusion, the specter of AI-generated spam inundating Google’s search results poses an existential threat, prompting Google’s decisive action. This crackdown not only serves as a punitive measure but also sends a clear message regarding Google’s stance on AI-generated spam, signaling a concerted effort to preserve the integrity of its search ecosystem