How VR Healthcare is Pioneering a Healthy Future

The emergence of virtual reality technology has had a profound impact across an array of industries – perhaps none more so than that of healthcare in recent years. Now, as the vast potential of the metaverse edges closer to reality, VR healthcare may be catapulted into everyday use cases.
What’s more, is that the growing VR healthcare market is set to be big business for companies that embrace technology quickly.
(Image: Yahoo Finance)
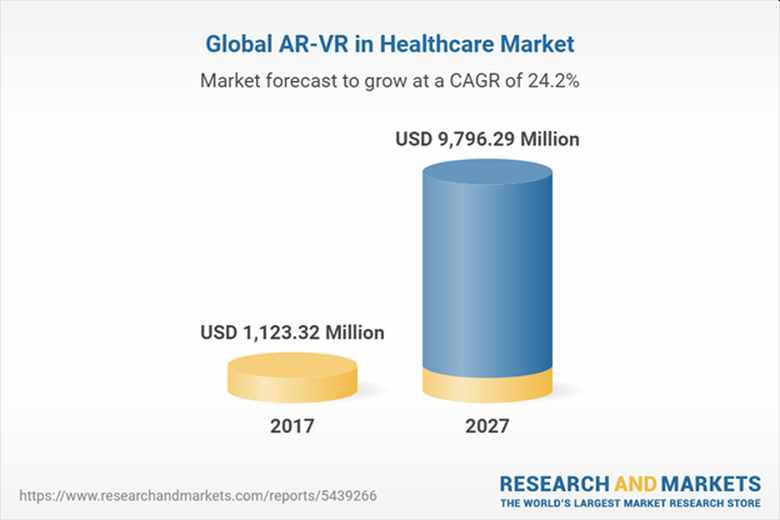
According to data compiled by Research and Markets, the reality technology healthcare market has been forecast to grow at a CAGR of 24.4% to reach a value of almost $10 billion by 2027 – representing an increase of almost 10-times its value in 2017.
Already we’re seeing both virtual and augmented reality applications within the industry, and in June 2022, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted OxfordVR a device designation for its game-changer VR platform designed to treat users suffering from schizophrenia and other mental illnesses.
OxfordVR’s game-Change VR platform is just one recent example of how virtual reality is capable of delivering comprehensive and immersive levels of treatment to patients in a way that’s previously been inaccessible.
Today, as the metaverse embarks on its development towards an essential Web3 service for health-conscious users, we’re already seeing the potential of virtual reality being realized within the sector. Particularly in the field of staff training.
The Rise of VR Healthcare Training
In recent years, the world of healthcare has sought to take a leaf out of the aviation industry’s book in terms of embracing virtual and augmented reality for simulation-based training purposes. Given the high levels of risk associated with both industries, embracing reality technology has been a seamless fit for those learning the ropes. In the future, it seems certain that we will see a new form of educational landscape emerge within the metaverse for trainees in professions that carry a high margin for error.
“With no standard definition yet, the metaverse means different things to different people depending on the nature of their business. However, GlobalData defines the metaverse as a virtual world where users share experiences and interact in real-time within simulated scenarios,” said Rupantar Guha, Project Manager at GlobalData.
Reality technology can perform many useful functions when it comes to medical training. The human body can be accurately mapped in 3D in rich detail. This can not only help students to study but can also aid hands-on surgeon training programs without the need for bringing real patients into the fray until an aptitude is developed.
We’ve already seen a collection of immersive virtual reality training platforms generate significant levels of funding in building a product that’s ready for market. For instance, FundamentalVR raised $20 million in August for its immersive simulation platform for medical and healthcare professions. The program has been developed to “accelerate skill transfer and surgical proficiency” through reality technology applications.
Healthcare in the Age of the ‘Mediverse’
“You may have heard of the Metaverse,” said Azize Naji, the founder of Welsh startup, Goggleminds. “We’ve taken it one step further with the ‘Mediverse’.”
The idea behind the Mediverse is that it can act as a digital platform for medical VR training and collaborative interconnectivity between professionals on a scale that’s never before been possible. Unlike the medical VR training apps that are prevalent today, the Mediverse will be accessible for professionals and medical students from anywhere, and it will be possible for users to connect with each other on a national and international level.
The Mediverse is just a taste of the scale of what the arrival of the metaverse can bring healthcare professionals, students, and patients alike.
Packed inside this sprawling, distributed virtual landscape can be a range of healthcare-related constructs, learning platforms, and VR treatment opportunities – all encased within a digital health district.
Notably, Latus Healthcare is already developing one of the metaverse’s first ‘virtual hospitals’ for patients, which will be characterized by a realistic hospital environment that offers physiotherapy-related treatments to users.
Elsewhere in the Decentraland Metaverse, iMining has become the first hospital launched within the virtual ecosystem, whilst Apollo Hospitals has committed to investing in its own healthcare-oriented metaverse in collaboration with 8chili Inc.
These examples of metaverse healthcare are certainly not isolated, and we can expect countless more innovative and intricate endeavors to be launched as metaverse technology matures. With dedicated metaverse construction and VR development studios like the London-based BORN working with clients hailing from a range of industries, it’s likely that healthcare in the age of Web3 will be competitive and diverse.
As the popularity of the metaverse and the convenience it will bring to potentially billions of users continues to grow, we may see the rise of the virtual, avatar-based landscape embolden more users to seek medical advice for discomforts and ailments. Rather than calling or visiting a doctor, the ease of navigating to a trusted healthcare location in the metaverse can be the most effective means of getting valuable diagnoses quickly.
Should treatment be required, patients can then rest easy knowing that they’re in safe hands with highly VR-trained doctors and surgeons.

