Crypto miners are the most common web threats with over 170K unique malicious URLs, new internet security threat report shows

For many years most common web threats come from a few malware families that share common characteristics including viruses, social engineering, malicious code, exploits, and cybercrimes. But that’s changing according to a new cybersecurity threat report.
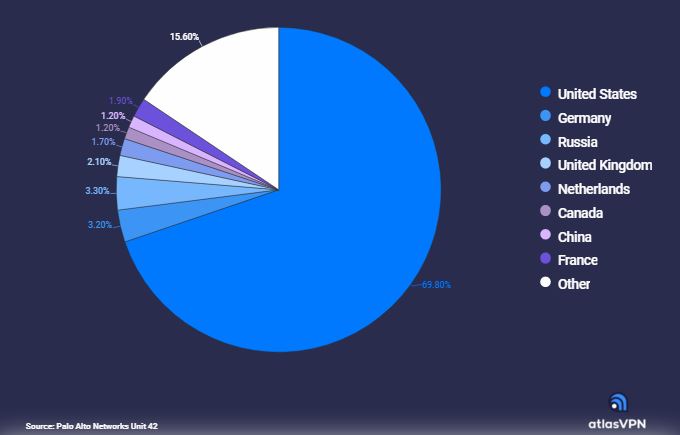
According to the data presented by the Atlas VPN team, 177,753 unique URLs with crypto miners posed web threats from October 2020 to September 2021. Furthermore, nearly 70% of all detected web threat domains appear to be located in the United States.
The data is based on Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 research, The Year in Web Threats: Web Skimmers Take Advantage of Cloud Hosting and More. The report observed and analyzed web threats trends between October 2020 and September 2021.
Report Highlights:
• A total of 177,753 unique URLs with crypto miners caused 652,907 threats on the web.
• 147,918 unique URLs with JavaScript (JS) downloaders were observed between October 2020 and September 2021, accumulating 712,023 total threats.
• 147,907 unique URLs with web skimmers accumulated a total of 611,811 web threats.
• From October 2020 to September 2021, a total of about 831K unique URLs were found to be posing web threats.
• The URLs are from nearly 52K unique domains, of which the majority, almost 70%, seem to originate from the United States.
Web threats frequently infiltrate users’ networks without their knowledge and can be triggered by opening a spam email or clicking on an executable file attachment.
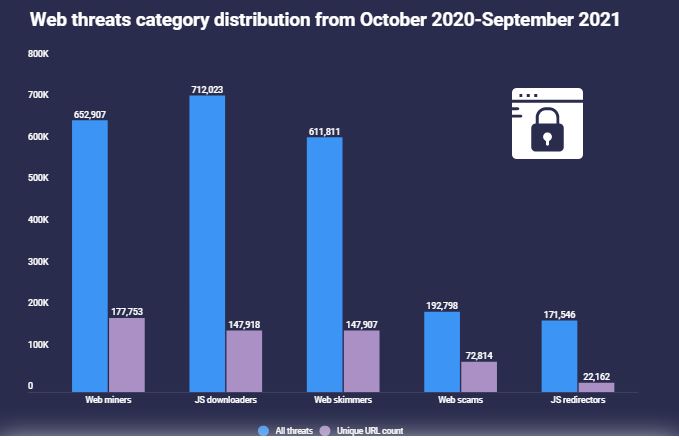
A total of 177,753 unique URLs with crypto miners caused 652,907 threats on the web. Cryptocurrency miners that run in web browsers consume significant CPU resources, making computer use extremely slow.
Following up, 147,918 unique URLs with JavaScript (JS) downloaders were observed between October 2020 and September 2021, accumulating 712,023 total threats. JS downloaders are snippets of JavaScript code that download malicious codes files from websites remotely to enable other harmful behaviors.
Next up, 147,907 unique URLs with web skimmers accumulated a total of 611,811 web threats. Web skimming is a hacking technique where the cybercriminal embeds a snippet of JavaScript code into e-commerce or banking web pages to steal sensitive user information such as credit card information and personally identifiable information (PII).
Cybersecurity writer at Atlas VPN Vilius Kardelis shares his thoughts on web threats: “The danger of web threats highlights that website administrators must patch all systems, components, and web plugins to help minimize the risks of compromised systems. From the side of internet users, they should stay vigilant online and avoid clicking suspicious links and emails to prevent malware infection.”
Web threats origins
Malicious URLs are hosted on domains whose origins can be traced by identifying the geographical locations for the domain names. However, it is essential to recognize that many cybercriminals could be using leverage proxy servers and VPNs to change their IP addresses from their actual physical locations.
From October 2020 to September 2021, a total of about 831K unique URLs were found to be posing web threats. The URLs are from nearly 52K unique domains, of which the majority, almost 70%, seem to originate from the United States.
Russia follows up in second place as 3.3% of domains carrying malicious URLs were located there. A bit less, 3.2% of unique domains containing harmful URLs appeared to be found in Germany.
Finally, the rest of the domains, 15.6% to be exact, appeared to be found in other countries.
You can see the full report here.

