The 760 miles per hour Hyperloop could become the fastest way to travel and forever change the future of transportation
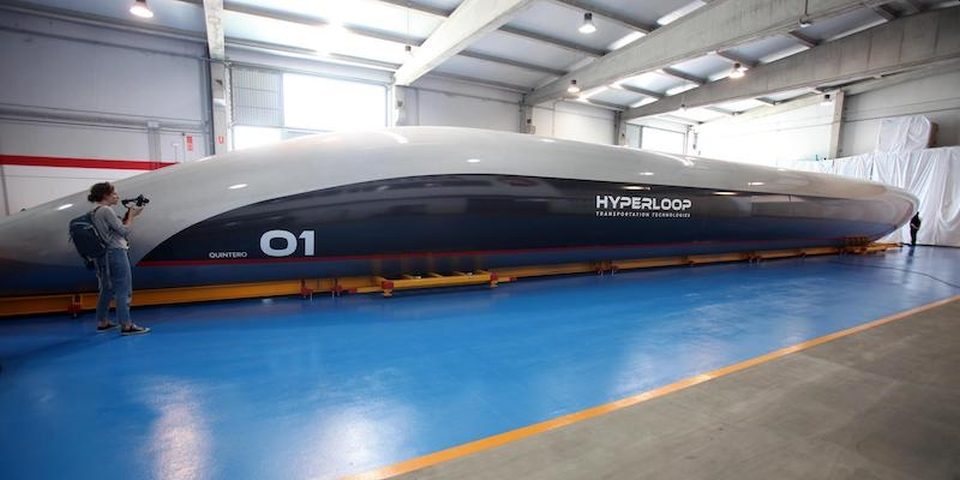

Hyperloop is a new mode of ground transportation that could make it possible for passengers to travel at over 700 miles an hour in a floating pod that travels inside giant low-pressure tubes, either above or below ground.
Unlike the current traditional mode of transportation, the hyperloop capsules or pods carrying passengers travel through nearly airless tubes or tunnels to reduce friction, which allows the pods to travel at up to 750 miles per hour. In addition, the hyperloop uses less energy per passenger than train or airplane and is completely powered by renewable electricity with zero CO2 emissions.
The idea was first conceived by Tesla CEO Elon Musk in 2012. It was part of Musk’s effort to bring about his industrial experiment to build high-speed underground transportation systems in dense urban regions. In August 2013, SpaceX and Tesla CEO published a white paper that describes hyperloop as a super-fast passenger train that would overcome the usual friction by levitating above its track on air-bearings in an enclosed low-pressure tube.
Even though Musk was the first to propose the idea, his company, Boring Company was not the first company to test the technology. On November 8, 2020, Virgin Hyperloop became the first and only company in the world to successfully test hyperloop technology with passengers, launching the first new mode of mass transportation in over 100 years.

According to the company, the hyperloop system can propel passenger or cargo pods at speeds of over 670 miles per hour (or 1000 km/h), which is 3 times faster than high-speed rail and more than 10 times faster than traditional rail. However, its first passenger test fell short of the ambitious speed. The Virgin Hyperloop test run was on a 500-meter track north of Las Vegas.
The Hyperloop reached a maximum speed of 100 mph with two people riding through a hyperloop Pegasus pod through a nearly airless tube. Hyperloop pod managed to reach speeds of up to 288 mph without any passengers.
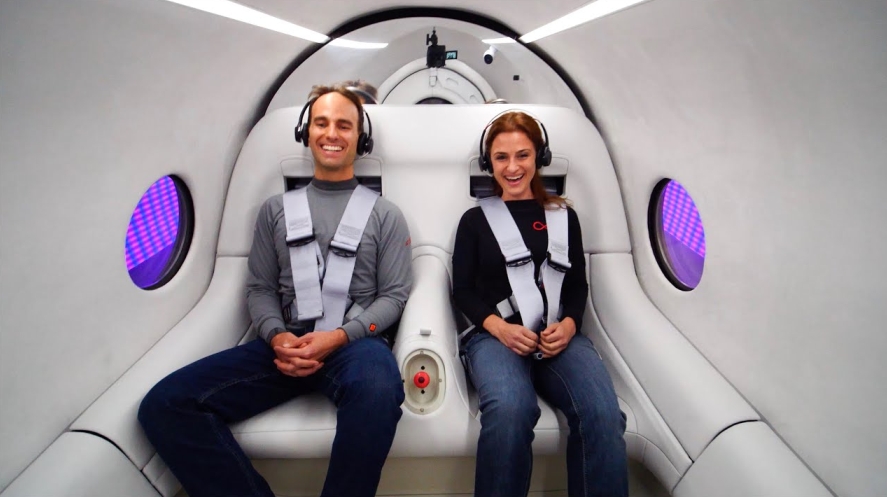
Josh Giegel and Sara Luchian.Virgin Hyperloop
Virgin Hyperloop said it expects to reach the top speed for its passenger or freight cargo Pegasus pods to reach 650 mph in the future. As of May 2019, Hyperloop One has raised around $400 million from several investors including Sherpa Capital, Formation 8, Khosla Ventures, GE Ventures, and others.
Meanwhile, Virgin Hyperloop and Elon Musk’s Boring Company are not the only two companies working on hyperloop technology. In May 2016, The MIT Hyperloop team unveiled the first Hyperloop pod prototype at the MIT Museum. Their design uses electrodynamic suspension for levitating and eddy current braking.
Separately, there are also a couple of other startup visionaries in Europe working on the same technology. Hyperloop Transportation Technologies (HyperloopTT) is another startup working to connect cities in France. The startup currently has over 800 engineers working in a worldwide network on the implementation of the hyperloop system.
In 2018, HyperloopTT began the construction of the world’s third Hyperloop Transportation Technologies built a complete test system for its transport capsules in Toulouse, France. It was construction the first in Europe. With plans to carry up to 50 passengers per capsule, HyperloopTT said the capsules will travel up to 745 miles per hour (1,200 kilometres per hour) on a magnetic track. According to HyperloopOne, the track will be built in two phases. A 320-meter system is expected to be completed this year, another kilometer-long full-scale system is expected by next year.
In July 2020, another Dutch tech startup Hardt completed a 30-meter-long section of track in the province of South Holland. Hardt said it plans to develop a 10,000 kilometers hyperloop network crossing national borders.
Below is a video of hyperloop works.
Below is Virgin Hyperloop passenger test.
https://youtu.be/xKvbSboQ5_g

