Scientists Print Magnetic Liquid Droplets, a revolutionary material that could lead to 3D-printable magnetic liquid devices for flexible electronics and artificial cells
Everyday, we come into contact with magnets in the course of your daily life. Rare earth magnets play a significant role in a wide range of devices we use including toys, computers, credit cards, and MRI body scan machines.
All of these technologies rely on magnets made from solid materials. But what if you could make a magnetic device out of liquids? Using a modified 3D printer, a team of scientists at the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have done just that. Their findings, to be published July 19 in the journal Science, could lead to a revolutionary class of printable liquid devices for a variety of applications – from artificial cells that deliver targeted cancer therapies to flexible liquid robots that can change their shape to adapt to their surroundings.
“We’ve made a new material that is both liquid and magnetic. No one has ever observed this before,” said Tom Russell, a visiting faculty scientist at Berkeley Lab and professor of polymer science and engineering at the University of Massachusetts, Amherst, who led the study. “This opens the door to a new area of science in magnetic soft matter.”
For the past seven years, Russell, who leads a program called Adaptive Interfacial Assemblies Towards Structuring Liquids in Berkeley Lab’s Materials Sciences Division and also led the current study, has focused on developing a new class of materials – 3D-printable all-liquid structures.
Russell and Xubo Liu, the study’s lead author, came up with the idea of forming liquid structures from ferrofluids, which are solutions of iron-oxide particles that become strongly magnetic in the presence of another magnet. “We wondered, ‘If a ferrofluid can become temporarily magnetic, what could we do to make it permanently magnetic, and behave like a solid magnet but still look and feel like a liquid?’” said Russell.
Jam sessions: making magnets out of liquids
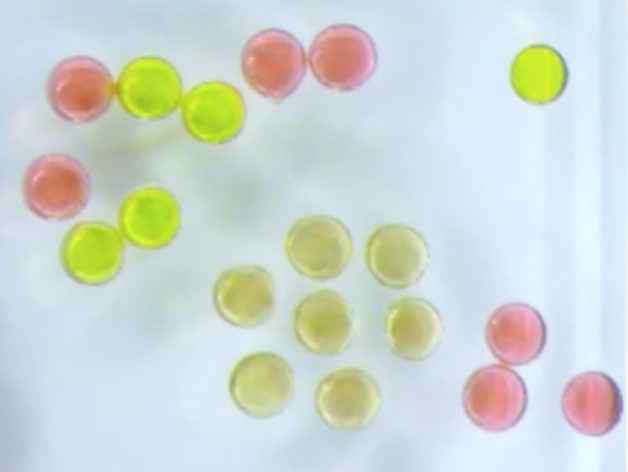
To find out, Russell and Liu used a 3D-printing technique they had developed with former postdoctoral researcher Joe Forth in Berkeley Lab’s Materials Sciences Division to print 1 millimeter droplets from a ferrofluid solution containing iron-oxide nanoparticles just 20 nanometers in diameter (the average size of an antibody protein).
Using surface chemistry and sophisticated atomic force microscopy techniques, staff scientists Paul Ashby and Brett Helms of Berkeley Lab’s Molecular Foundry revealed that the nanoparticles formed a solid-like shell at the interface between the two liquids through a phenomenon called “interfacial jamming.” This causes the nanoparticles to crowd at the droplet’s surface, “like the walls coming together in a small room jampacked with people,” said Russell.
To make them magnetic, the scientists placed the droplets by a magnetic coil in solution. As expected, the magnetic coil pulled the iron-oxide nanoparticles toward it.
But when they removed the magnetic coil, something quite unexpected happened.

