Biotech startup Cullgen raises $15 million to launch drug discovery platform based on advanced ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation technology
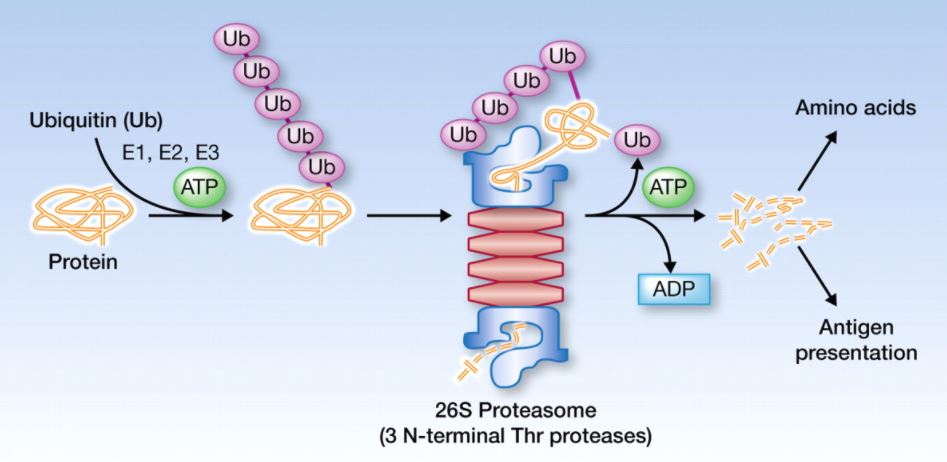
North Carolina-based Biotech startup, Cullgen, announced Thursday it has raised up to $15 million in Series Seed Financing from Japan GNI Group Ltd (GNI). The funding will be used to build a new drug discovery platform based on advanced ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation technology. GNI is a Japan-based multinational life-science company that focuses on pharmaceutical and medical device businesses with headquarters in Tokyo and subsidiaries in China and the United States.
Founded this year by team of scientists: Dr. Yue Xiong, William R. Kenan Professor of Biochemistry and Biophysics, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and Dr. Jian Jin, Professor of Pharmacological Sciences, Icahn School of Medicine, Mount Sinai, New York, Cullgen’s mission is to use a revolutionary technology to create, in a highly efficient manner, new drugs for treatment of diseases that currently lack effective therapies. Cullgen initial plan is to focus on oncology and immune diseases. Cullgen also intends to probe mechanisms of ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation and to develop additional technologies for identifying protein-small molecule interactions to discover new therapeutic targets and novel drug candidates.
On his University of North Carolina’s web page, Professor Yue Xiong describes the nature of the problems the company is trying to solve.
Most, if not all, cellular processes, including notably cell cycle control and p53 control, are regulated by ubiquitin-mediated modification and degradation. The mechanisms targeting specific proteins for ubiquitylation, in most cases, are poorly understood. We discovered two novel RING finger proteins, ROC1 and ROC2, which constitute active ubiquitin ligases with members of the cullin family. We also discovered that Cullins 3 and 4 could assemble in vivo as many as 200 and 100 distinct E3 ubiquitin ligases, respectively. Our current research in this area is focused on two issues. (1) Developing a strategy to systematically identify the substrates of the cullin-RING E3 ligases, and (2) Elucidating the mechanism of CUL4 E3 ligases in control of gene expression and chromatin structure.
(Mol. Cell 3:535;Mol. Cell 10:1511; Nat. Cell Biol. 5:1001, Nat Cell Biol 6:1003; Genes Dev. 20:2949; Genes Dev. 22:866; Science 324:261).
(A, B) Cullins bind to a RING finger protein, ROC1 or ROC2, which brings in and activates E2 ubiquitin conjugating enzymes. CUL3 binds with BTB domain and CUL4 interacts with WD40 repeats via DDB1. Various BTB and WD40 containing proteins recruit different substrates for the ubiquitylation by CUL3-ROC and CUL4-ROC E3 ligases. Mammalian cells express 200 BTB and 300 WD40 proteins. (C) CUL7 and CUL9 both localize in the cytoplasm, and bind with ROC and p53. The functions and mechanisms of both CUL7 and CUL9 in the cell cycle and p53 control are not clear.
Cullgen’s technology focuses on selective degradation of disease-causing proteins, including targets previously considered undruggable. This technology can provide scientists with new means to develop novel therapeutic approaches for various diseases. Since 1998, Dr. Xiong has been among the first to discover the catalytic and regulatory components and the assembly mechanism of the cullin-RING family of E3 ubiquitin ligases, enzymes that comprise the basis of Cullgen’s technology platform. During the past several years, Dr. Jin and Dr. Xiong have successfully developed many new chemical entities (NCEs) against different cancer targets, which has resulted in multiple patent applications. This new drug discovery platform has the advantage of accelerating NCEs into clinical development in a cost and time efficient manner to benefit patients. Initial drug discovery programs will focus on oncology and expand into areas such as inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.
To-date, Cullgen has invited Dr. Lisa Carey, Dr. Stephen Frye, and Dr. Peter Jackson, to join the company’s scientific advisory board. They bring extensive experience and achievements in medical oncology, drug discovery and ubiquitin research.
Cullgen’s Board of Directors includes Dr. Ying Luo, President and CEO of GNIG, Dr. Yue Xiong, Dr. Jian Jin, and Mr. Thomas Eastling, CFO of GNIG. Other board members and corporate executives will be appointed in the future.