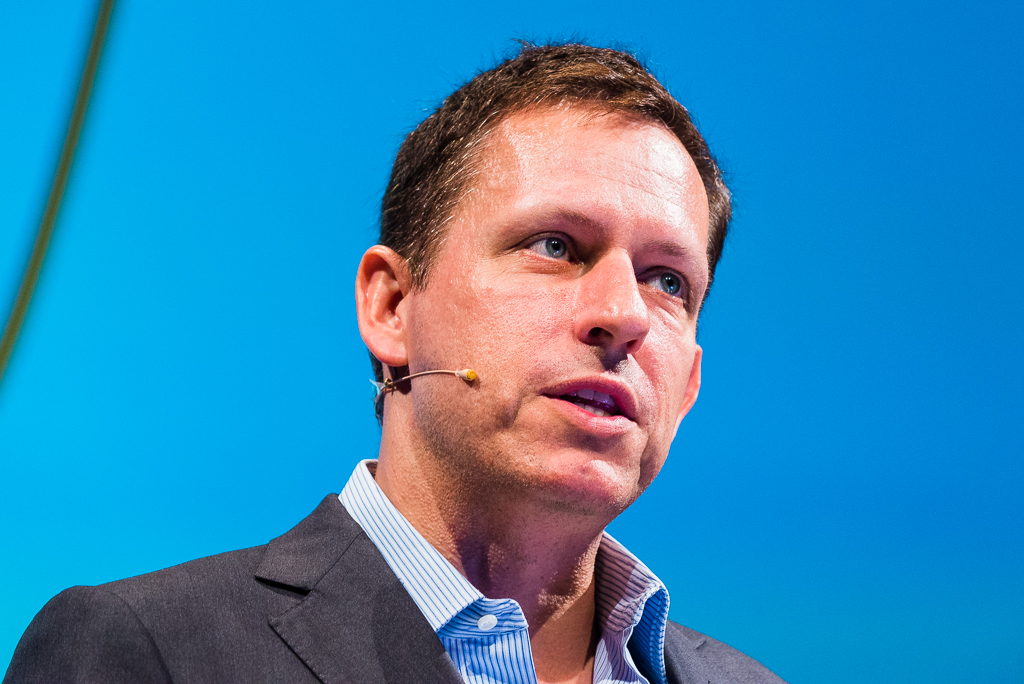
Government remotely hacked a Boeing 757
An official at the Department of Homeland Security admitted that a team of experts remotely hacked a Boeing 757 parked at an airport. The hack was not conducted in a laboratory, but on a 757 parked at the airport in Atlantic City, N.J. And the actual hack occurred over a year ago. We are only now hearing about it thanks to a keynote delivered by Robert Hickey, aviation program manager within the Cyber Security Division of the DHS Science and Technology (S&T) Directorate.
A team of government, industry and academic officials successfully demonstrated that a commercial aircraft could be remotely hacked in a non-laboratory setting last year, a U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS) official said Wednesday at the 2017 CyberSat Summit in Tysons Corner, Virginia.
“We got the airplane on Sept. 19, 2016. Two days later, I was successful in accomplishing a remote, non-cooperative, penetration,” said Robert Hickey, aviation program manager within the Cyber Security Division of the DHS Science and Technology (S&T) Directorate.
“[Which] means I didn’t have anybody touching the airplane, I didn’t have an insider threat. I stood off using typical stuff that could get through security and we were able to establish a presence on the systems of the aircraft.” Hickey said the details of the hack and the work his team are doing are classified, but said they accessed the aircraft’s systems through radio frequency communications, adding that, based on the RF configuration of most aircraft, “you can come to grips pretty quickly where we went” on the aircraft.
The aircraft that DHS is using for its tests is a legacy Boeing 757 commercial plane purchased by the S&T branch. After his speech at the CyberSat Summit, Hickey told Avionics sister publication Defense Daily that the testing is with the aircraft on the ground at the airport in Atlantic City, New Jersey. The initial response from experts was, “’We’ve known that for years,’” and, “It’s not a big deal,” Hickey said.
