Bill of Materials (BOM): Step-by-Step Guide & Best Practices

A Bill of Materials (BOM) is a detailed list of everything needed to build a product. This document is essential for accurate production planning, smooth inventory management, and efficient manufacturing operations. In this guide, we’ll explore what makes up a BOM, its different types, and best practices for creating and managing one.
Understanding the Bill of Materials (BOM)
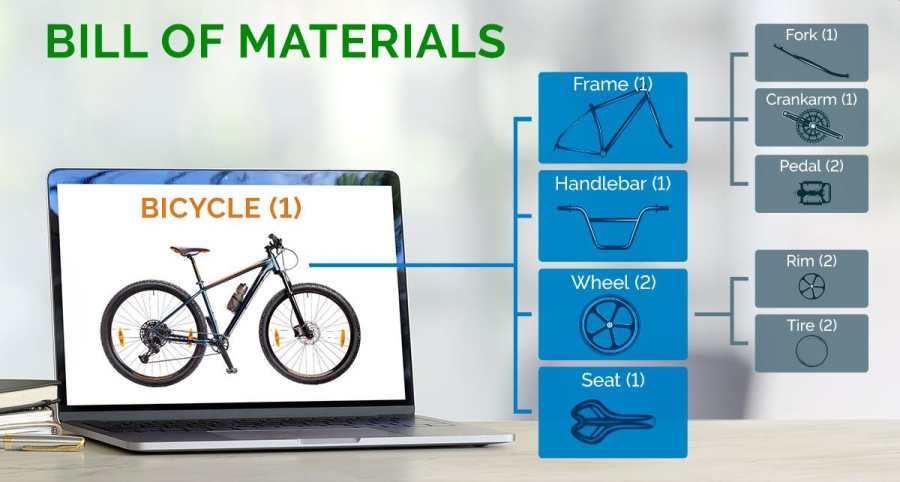
A Bill of Materials (BOM) is more than just a list; it’s a detailed document that enumerates all the materials and components needed to create a product. Whether you’re in manufacturing, engineering, or sales, the BOM is a cornerstone document that ensures everyone is on the same page. Effective configuration management through a BOM ensures accurate definitions flow seamlessly downstream, minimizing errors and delays.
A manufacturing bom acts as an instruction manual for the production line, directing material procurement and component assembly. It’s central to product development, quality assurance, and inventory management. Imagine trying to assemble a complex piece of machinery without knowing the exact parts needed or their quantities—chaos would ensue. A well-managed manufacturing boms helps avoid such pitfalls by providing a detailed plan for production and material usage.
Managing a BOM effectively is crucial, regardless of product size or complexity. It minimizes the risk of material shortages or overages, ensures timely ordering of replacements, and maintains the integrity of tools and components throughout the production lifecycle. In short, the BOM is indispensable for smooth, efficient, and cost-effective manufacturing operations.
Core Components of a Bill of Materials
A comprehensive Bill of Materials (BOM) includes several core components such as product codes, part descriptions, quantities, pricing, and costs. These elements ensure that every aspect of the production and procurement processes is meticulously planned.
We’ll break down these core components into three main categories: Part Numbers and Descriptions, Quantities and Units of Measure, and Costs and Procurement Types.
Part Numbers and Descriptions
Unique identifiers for each part or assembly are crucial to maintaining consistency and accuracy in procurement and production. Each item in a BOM is displayed alongside its SKU (Stock Keeping Unit), providing a unique identifier that aids in tracking and managing inventory. This helps prevent confusion and ensures that the correct parts are ordered and used.
In complex assembly process, part classification and unique naming conventions are vital. They streamline part identification and ensure that different materials are accurately distinguished.
In multi-level BOMs, item numbers are structured to link to a parent item, establishing clear component-assembly relationships.
Quantities and Units of Measure
Specifying the quantity of each part in a BOM is essential for accurate procurement and efficient production. The quantity indicates the number of parts used in an assembly, ensuring that enough materials are available for the entire production run. This helps establish reorder points and prevents production delays due to material shortages.
The unit of measure designates how parts are quantified for procurement and usage. Whether measured in pieces, kilograms, or meters, specifying the unit of measure ensures that the right quantities are ordered and used during the manufacturing process.
Effective management of quantities and units of measure leads to more accurate BOMs, which are crucial for maintaining high product quality and manufacturing efficiency.
Costs and Procurement Types
A well-constructed BOM lists the costs for materials, parts, or components, facilitating precise material planning and accurate cost estimation. This aids effective financial planning and resource allocation in manufacturing. Inventory management software can automatically fill in stock costs based on the quantity entered, streamlining the process.
Different levels of a multi-level BOM can include information about cost, lead time, and work processes. This ensures that all aspects of the procurement process are considered, from initial purchase to final assembly.
Accurate cost estimation and procurement details are essential for maintaining budgetary control and ensuring the financial viability of manufacturing projects.
Types of Bills of Materials
Bills of Materials (BOMs) come in various types, each serving specific functions in product assembly and management. Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the right engineering bom structure for your needs.
The most common types include Single-Level, Multi-Level, and Configurable BOMs, each offering different levels of detail and complexity.
Single-Level Bill of Materials
A Single-Level Bill of Materials (BOM) is akin to a shopping list, detailing all parts required for a product. It’s best suited for products with uniform features and fewer components, such as an office desk with a wooden top and steel frame. This straightforward approach simplifies materials management and is ideal for companies with simple products or minimal downstream sub-processing.
However, Single-Level BOMs have their limitations. They don’t specify relationships between parent and child parts, making them less suitable for complex products. If a product fails, identifying which material needs replacement can be challenging. Despite these drawbacks, Single-Level BOMs are effective for straightforward production processes where components and quantities remain consistent across units.
An example of a Single-Level BOM is the construction of a basic office desk. The BOM would list the wooden top, steel frame, screws, and other necessary components, along with their quantities and part numbers. This simple structure ensures that all required parts are accounted for, facilitating efficient production.
Multi-Level Bill of Materials
A Multi-Level Bill of Materials (BOM) provides a hierarchical structure that details parent-child relationships among components and sub-assemblies. This type of BOM offers greater detail and specificity, making it ideal for complex products that require multiple layers of components. It’s akin to a family tree, mapping out the intricate relationships between parts and sub-assemblies.
The main advantage of a Multi-Level BOM is its ability to maintain product structures, making it easier to manage complex assemblies. This detailed approach is particularly useful for products like printed circuit board assemblies, where intermediate assemblies and sub-components need to be meticulously tracked. However, the complexity of Multi-Level BOMs requires more rigorous management and documentation.
For example, a Multi-Level BOM for a bicycle would not only list the frame and wheels but also break down the wheels into tires, spokes, and hubs. This detailed structure helps in managing inventory, planning production, and ensuring that each sub-assembly is correctly assembled.
Configurable Bill of Materials
A Configurable Bill of Materials (CBOM) is designed for products that can be customized to meet specific customer requirements. This type of BOM is essential for managing products with variations in parameters such as size, color, or additional features. It allows manufacturers to efficiently handle a wide range of product configurations without needing separate BOMs for each variant.
One of the primary benefits of a Configurable BOM is its modular structure, which provides assemblies or subsystems that can be configured into an end item. This structure reduces the work effort needed to maintain product structures and enhances operational efficiency. For instance, a furniture manufacturer might use a Configurable BOM to offer coffee tables in various colors and finishes without creating multiple BOMs.
Industries such as job shops and heavy machinery, where product specification variability is high, frequently use Configurable BOMs. This approach allows for easy management of products with variations, streamlining the production process and improving customer satisfaction.
Benefits of Using an Effective BOM

Using an effective BOM offers numerous benefits, from improving efficiency to reducing waste. A well-managed BOM enhances inventory management by preventing both shortages and overstock situations, ensuring that production runs smoothly. It also supports production planning by providing detailed documentation of product modifications, which is crucial for maintaining production schedules and quality standards.
Moreover, an effective BOM facilitates better coordination between departments, enhancing overall communication and production accuracy. By standardizing material usage, a BOM minimizes waste and ensures that resources are utilized efficiently. This not only helps in cost control but also contributes to higher product quality and customer satisfaction.
Challenges in BOM Management
Managing a Bill of Materials (BOM) comes with its own set of challenges, especially given the complexity of modern products. One of the primary issues is the integration of multiple components, which can lead to errors and inefficiencies if not managed properly. Manual data entry and siloed tools often exacerbate these problems, resulting in mistakes that can disrupt the production schedule.
Errors in quantity calculations and poor documentation are other common challenges that can lead to costly delays and reduced product quality. It’s essential to organize and regularly update BOMs to reflect changes in production requirements. Without adequate product documentation, safety can be compromised, and revenue loss may occur due to delays and waste.
Best Practices for Creating an Accurate BOM
Overcoming BOM management challenges requires adherence to best practices for accuracy and efficiency. These practices include centralizing control of the BOM, tracking revisions and changes meticulously, and utilizing specialized software.
Let’s delve into each of these best practices.
Centralize Control of the BOM
Centralizing BOM data allows for a single, accurate record from various departments, facilitating better collaboration and communication. Using a central hub for BOM documentation provides unlimited file storage, central access to BOM, and enables change requests, streamlining the entire materials management process. This approach not only aids in maintaining an accurate BOM but also enhances inventory management and quality control.
A centralized BOM system simplifies invoice management and ensures all stakeholders have access to the latest information. This reduces the risk of errors and ensures that the manufacturing process runs smoothly, from procurement to production.
Track Revisions and Changes
Maintaining BOM integrity and ensuring accountability requires meticulous tracking of changes. A version control system provides a history of changes, making it easier to trace any modifications and understand their impact on the production process. This transparency is crucial for effective BOM management and helps in identifying any discrepancies or errors in the documentation.
Implementing a robust version control system ensures that all changes are documented and easily accessible. This not only aids in maintaining an accurate BOM but also supports continuous improvement in the manufacturing process by providing valuable insights into past changes and their outcomes.
Utilize Specialized Software
Dedicated BOM management tools can greatly enhance the efficiency of the BOM creation process. These tools offer features like automated error checking and seamless integration with existing systems, making it easier to manage complex BOMs. For instance, computer-aided design (CAD) tools are often used to support engineers in creating accurate and detailed BOMs.
Specialized software systems can also provide in-depth data analysis, helping manufacturers optimize their production processes and improve overall efficiency. Leveraging these tools ensures BOMs are accurate, current, and aligned with production goals.
Free Bill of Materials Template
A free Bill of Materials template is available to assist in planning purchases, estimating costs, controlling inventory, and minimizing production delays. This Excel template helps users list materials, parts, and components needed for manufacturing, including automatic calculation of unit and total costs. Whether you’re creating a single-level or multi-level BOM, this template can be customized to suit your specific project needs.
The template serves as a valuable tool for improving the materials management process, ensuring that all required raw materials are accounted for and accurately cost. This template helps manufacturers streamline procurement processes and enhance production efficiency.
Real-World Examples of BOMs
To understand the utility and versatility of a BOM, consider these real-world examples.
Consider a single-level BOM for a bicycle. This BOM would list components such as:
- the frame
- wheels
- handlebars
- seat
Along with their respective costs, totaling $199. The simplicity of this BOM makes it easy to follow and execute, ideal for straightforward products with limited components.
On the other hand, a multi-level BOM adds layers of complexity. For instance, a multi-level BOM for an electronics company producing 10,000 phones would detail sub-assemblies like the motherboard, which includes chips, resistors, and capacitors. This intricate structure ensures every part is accounted for, facilitating meticulous planning and inventory management.
Breaking down products into sub-components allows manufacturers to manage resources more effectively and reduce inefficiencies in the finished product through product lifecycle management.
Optimizing Production Efficiency With BOMs
Effective BOM management is a cornerstone of optimizing production efficiency and cost control. Standardizing material usage with BOMs minimizes waste and ensures judicious resource use. This not only leads to cost savings but also enhances product quality. Integration with ERP systems further optimizes production by leveraging BOM data for better forecasting and planning.
Configurable BOMs play a crucial role in managing product variations efficiently. Instead of creating separate BOMs for each variant, configurable BOMs allow manufacturers to handle different configurations within a single framework. This flexibility is particularly beneficial in industries with high product variability, enabling manufacturers to meet diverse customer needs without compromising on efficiency.
Integrating BOM with ERP Systems

Integrating a Bill of Materials with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems significantly enhances data management efficiency across product development and manufacturing. This integration centralizes BOM data, improving collaboration and communication between departments. Linking BOMs to ERP systems streamlines supply chain processes, ensuring accurate data flow and reducing overstock or stockout risks.
Real-time tracking of inventory levels is another major benefit of integrating BOM with ERP systems. This capability allows manufacturers to accurately forecast material needs and streamline procurement processes.
OpenBOM, a global collaborative Software as a Service platform, exemplifies this integration by managing data, product development lifecycle, production planning, and connecting manufacturers with their customers, contractors, and suppliers. OpenBOM helps build products faster with accurate data by managing CAD, parts, documents, BOMs, vendors, inventories, and purchases.
This powerful cloud-based platform integrates with existing tools, bringing product information together into a single source of truth, thus enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Summary
In summary, a well-constructed and meticulously managed BOM is essential for efficient manufacturing operations. From understanding the core components to exploring different types of BOMs, this guide has provided a comprehensive overview of how to create and manage an effective BOM. The benefits of using an accurate BOM are manifold, including improved efficiency, reduced waste, and better inventory management.
By following best practices such as centralizing BOM control, tracking revisions, and utilizing specialized software, manufacturers can overcome common challenges and optimize their production processes. Integration with ERP systems further enhances these benefits, ensuring seamless data flow and real-time inventory tracking. Implementing these strategies will not only streamline your manufacturing operations but also pave the way for higher product quality and customer satisfaction.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does BOM bill of materials consist of?
A bill of materials (BOM) consists of a detailed list of raw materials, parts, assemblies, subassemblies, and their respective quantities needed to manufacture a product, typically presented in a hierarchical format. Notably, it does not include labor costs.
What is a Bill of Materials (BOM)?
A Bill of Materials (BOM) is a comprehensive document that itemizes all materials and components required to manufacture a product. It serves as a crucial reference in the manufacturing process.
What are the core components of a BOM?
The core components of a Bill of Materials (BOM) are product codes, part descriptions, quantities, pricing, and costs. These elements are essential for precise planning in production and procurement activities.
What are the different types of BOMs?
The different types of BOMs include Single-Level BOM, Multi-Level BOM, and Configurable BOM, each designed for specific functions and varying in complexity and detail. Understanding these distinctions is essential for effective product management.
Why is it important to integrate BOM with ERP systems?
Integrating BOM with ERP systems is crucial as it enhances data management efficiency and improves collaboration, ultimately streamlining supply chain processes and enabling real-time inventory tracking. This integration leads to better decision-making and operational effectiveness.




