Deepseek, a free open-source AI model, outperforms OpenAI and Meta’s latest models at a fraction of the cost

Forget about ChatGPT. A new free AI large language model is taking the internet by storm. This new AI model doesn’t come from OpenAI, Meta, Google, or any familiar name. Meet DeepSeek, a free open-source AI developed by a Chinese startup. With 685 billion parameters, DeepSeek is capturing attention by outperforming nearly every model in the space.
The recent launch of DeepSeek’s latest version, V3, has captured global attention not only for its exceptional performance in benchmark tests but also for the astonishingly low cost of training its models.
A new report from CNBC reveals that DeepSeek-V3 surpasses models like Llama 3.1 and GPT-4o across various benchmarks. Trained on NVIDIA H800 GPUs at a fraction of the usual cost, it even hints at leveraging ChatGPT outputs (the model identifies as ChatGPT when asked). This development raises questions about the competitive edge of OpenAI and its dominance in frontier AI.
Why DeepSeek V3 Matters
According to multiple reports, DeepSeek V3 outperformed leading models like Llama 3.1 and GPT-4o on key benchmarks, including competitive coding challenges on Codeforces. The project was completed on a budget of just $5.5 million—a stark contrast to the hundreds of millions spent by its rivals. This breakthrough challenges the notion that cutting-edge AI development requires an enormous financial investment.
The model’s creators have openly stated that it leverages existing frameworks, potentially even ChatGPT outputs. This approach underscores the diminishing barriers to entry in AI development while raising questions about how proprietary data and resources are being utilized.
High Performance, Low Cost
DeepSeek’s ability to achieve world-class results on a limited budget has sparked debates among investors and engineers. CNBC’s Brian Sullivan highlighted the dramatic cost difference in a recent interview: “What am I getting for $5.5 million versus $1 billion?” The answer, according to analysts, is performance on par with some of the best models on the market. Third-party benchmarks confirm that DeepSeek V3 matches or surpasses its competitors in coding, translation, and text generation tasks.
Andrej Karpathy, a prominent figure in AI, called DeepSeek’s achievement a breakthrough in resource-efficient engineering. He noted that the model’s creators used just 2,048 GPUs for two months to train DeepSeek V3, a feat that challenges traditional assumptions about the scale required for such projects.
The Implications for AI Development
DeepSeek V3 is more than just a technical marvel; it’s a statement about the changing dynamics of the AI industry. Backed by High Flyer Capital Management, the project sidestepped restrictions on high-performance GPUs by using the more accessible NVIDIA H800s. The result? A model that delivers high-end capabilities without a high-end price tag.
Released under a permissive license, DeepSeek V3 allows developers to modify and integrate the model into commercial applications. Its open-source nature makes it accessible for tasks ranging from coding to content generation, potentially democratizing access to advanced AI tools.
DeepSeek Outperforms OpenAI GPT-4o and Meta Llama 3.1 in Performance Benchmarks

DeepSeek V3 has set new standards across various metrics. In coding challenges, it surpassed Meta’s Llama 3.1, OpenAI’s GPT-4o, and Alibaba’s Qwen 2.5. With its ability to process 60 tokens per second—three times faster than its predecessor—it’s poised to become a valuable tool for developers worldwide.
The model’s efficiency also raises important questions for investors. As the cost of training frontier models drops, will the high-end hardware race lose its relevance? DeepSeek V3’s success suggests that innovation and strategic resource use can outpace brute computational power.
An analysis conducted shows that while many models struggle with massive GPU demands and skyrocketing costs, DeepSeek-V3 has taken a smarter approach. Through innovative architectural and engineering methods, it has managed to deliver exceptional results without breaking the bank.
The V3 paper outlines that training the model required approximately 2.79 million GPU hours on NVIDIA H800s. At a rental rate of $2 per GPU hour, the total cost was just $5.58 million. Compared to the multi-billion-dollar budgets typically associated with large-scale AI projects, DeepSeek-V3 stands out as a remarkable example of cost-efficient innovation.
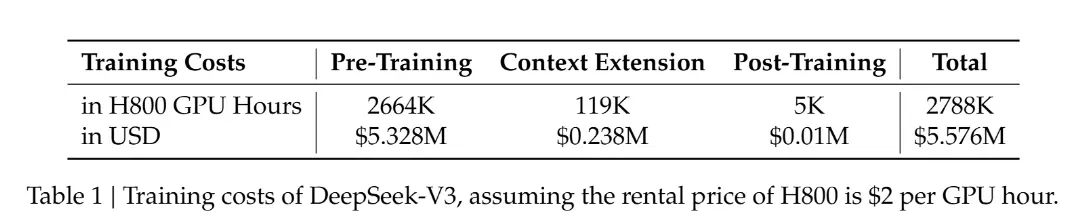
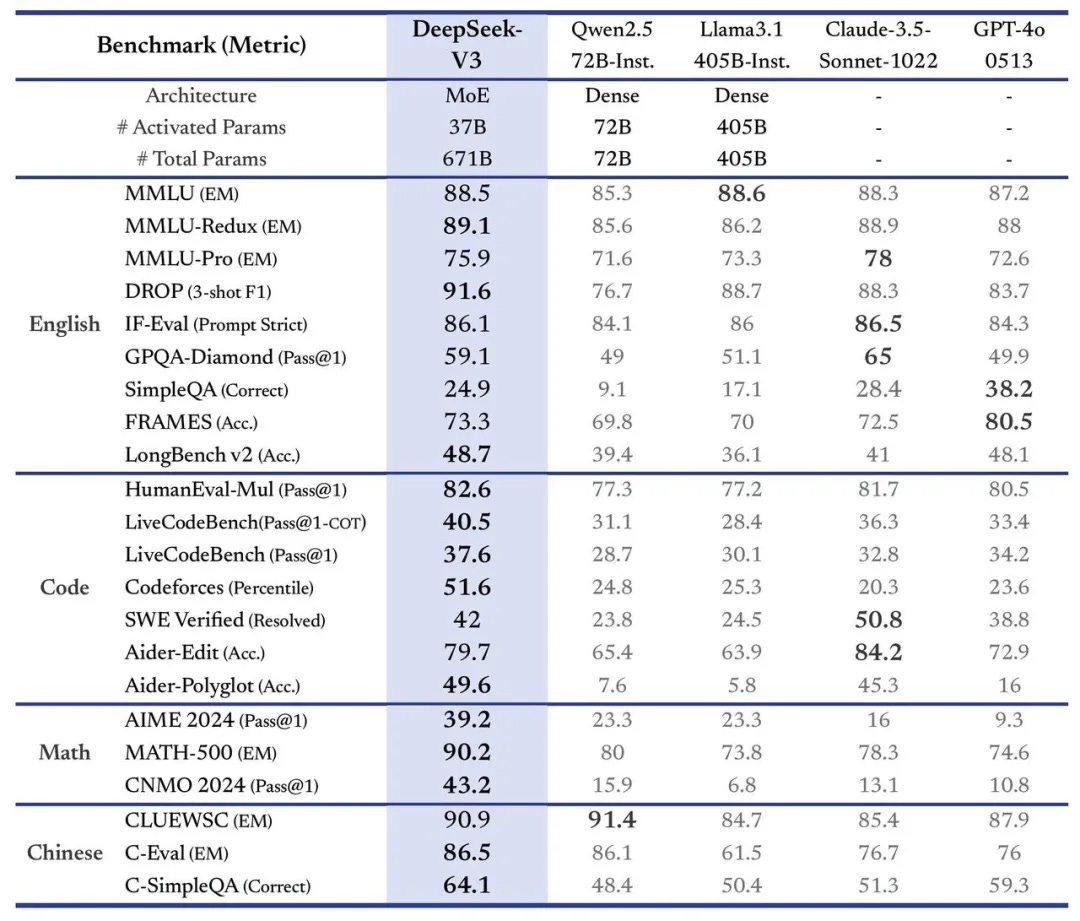
DeepSeek-V3 has proven its capabilities in several comparative tests, going toe-to-toe with leading models like GPT-4o and Claude 3.5. In areas such as code generation and mathematical reasoning, it has even outperformed some derivative versions of larger models across multiple metrics.
Andrej Karpathy, a well-known figure in AI, highlighted the achievement on social media, noting that V3 demonstrates how significant research and engineering breakthroughs can be achieved under tight resource constraints. This has sparked a broader conversation about whether building large-scale models truly requires massive GPU clusters. In a post on X, Karpathy said:
“DeepSeek (Chinese AI co) making it look easy today with an open weights release of a frontier-grade LLM trained on a joke of a budget (2048 GPUs for 2 months, $6M).”
DeepSeek (Chinese AI co) making it look easy today with an open weights release of a frontier-grade LLM trained on a joke of a budget (2048 GPUs for 2 months, $6M).
For reference, this level of capability is supposed to require clusters of closer to 16K GPUs, the ones being… https://t.co/EW7q2pQ94B
— Andrej Karpathy (@karpathy) December 26, 2024
This achievement stands out when compared to the usual expectations for such models, which often require clusters of 16,000 GPUs—or even up to 100,000 for the most advanced projects.
For example, Meta’s Llama 3.1 405B consumed 30.8 million GPU hours during training, while DeepSeek-V3 achieved comparable results with only 2.8 million GPU hours—an 11x reduction in compute. Early tests and rankings suggest the model holds up well, making it an impressive display of what’s possible with focused engineering and careful resource allocation.
This raises the question: do frontier-grade models require massive GPU clusters? While the answer isn’t a simple “no,” DeepSeek’s success underscores the importance of avoiding waste and optimizing both data and algorithms. It’s a clear reminder that there’s still untapped potential in refining existing methods and resources.
The Rise of Open-Source AI Models
DeepSeek V3 represents a shift in the AI ecosystem, proving that smaller players can compete with established leaders. Its performance, cost-efficiency, and open-source approach make it a model worth watching as it continues to challenge the status quo. Whether it’s a one-off achievement or a sign of things to come, DeepSeek V3 is reshaping how we think about AI development.
Meanwhile, DeepSeek isn’t the only Chinese AI model making waves. Just two weeks ago, Alibaba’s Qwen 2.5 grabbed attention by outperforming top U.S. closed-source models, including Anthropic’s Claude 3.5 Sonnet and OpenAI’s GPT-4o, in coding benchmarks. These developments highlight the growing competition from Chinese AI initiatives in pushing the boundaries of performance and innovation.
Watch the CNBC video below to see how the Chinese startup DeepSeek is shaking up the industry and challenging American AI dominance.




